How to Discover Yourself Using ChatGPT & LLMs: 25 Proven Techniques
Feb 4, 2026 | By Ahmed Sohail
They’re not just tools for writing emails or summarizing articles.
Over 800 million people now use ChatGPT weekly, but only a tiny fraction are using it for what might be its most powerful application – self-discovery and personal growth. According to OpenAI’s landmark 2025 study analyzing 1.5 million conversations, most usage focuses on everyday tasks and information seeking, while the profound introspective capabilities remain largely untapped.
And here’s the fascinating part: ChatGPT’s user base has evolved dramatically. In January 2024, only 37% of users were women. By mid-2025, that number jumped to 52% – suggesting people are discovering value beyond technical applications. Personal growth and self-reflection are driving this shift.
After spending hundreds of hours experimenting with various LLMs and analyzing real case studies of people who’ve experienced genuine breakthroughs, I’ve discovered 25 techniques that transform these AI systems from simple assistants into mirrors that reflect parts of yourself you’ve never seen before.
This isn’t about getting generic advice or surface-level affirmations.
This is about using advanced language models as sophisticated tools for deep self-reflection, pattern recognition, and authentic personal transformation.
Let me show you exactly how to do it.
Key Takeaways (Read This First)
-
800M+ weekly users but most miss ChatGPT's most powerful capability: deep self-discovery
-
Gender gap closed (37% → 52% women) as people discover personal growth applications
-
78% of AI journaling users report improved emotional regulation and reduced anxiety
-
Pattern recognition at scale - LLMs spot behavioral patterns across your life that take years of therapy to uncover
-
25 unique techniques below transform AI from assistant to mirror for authentic self-reflection
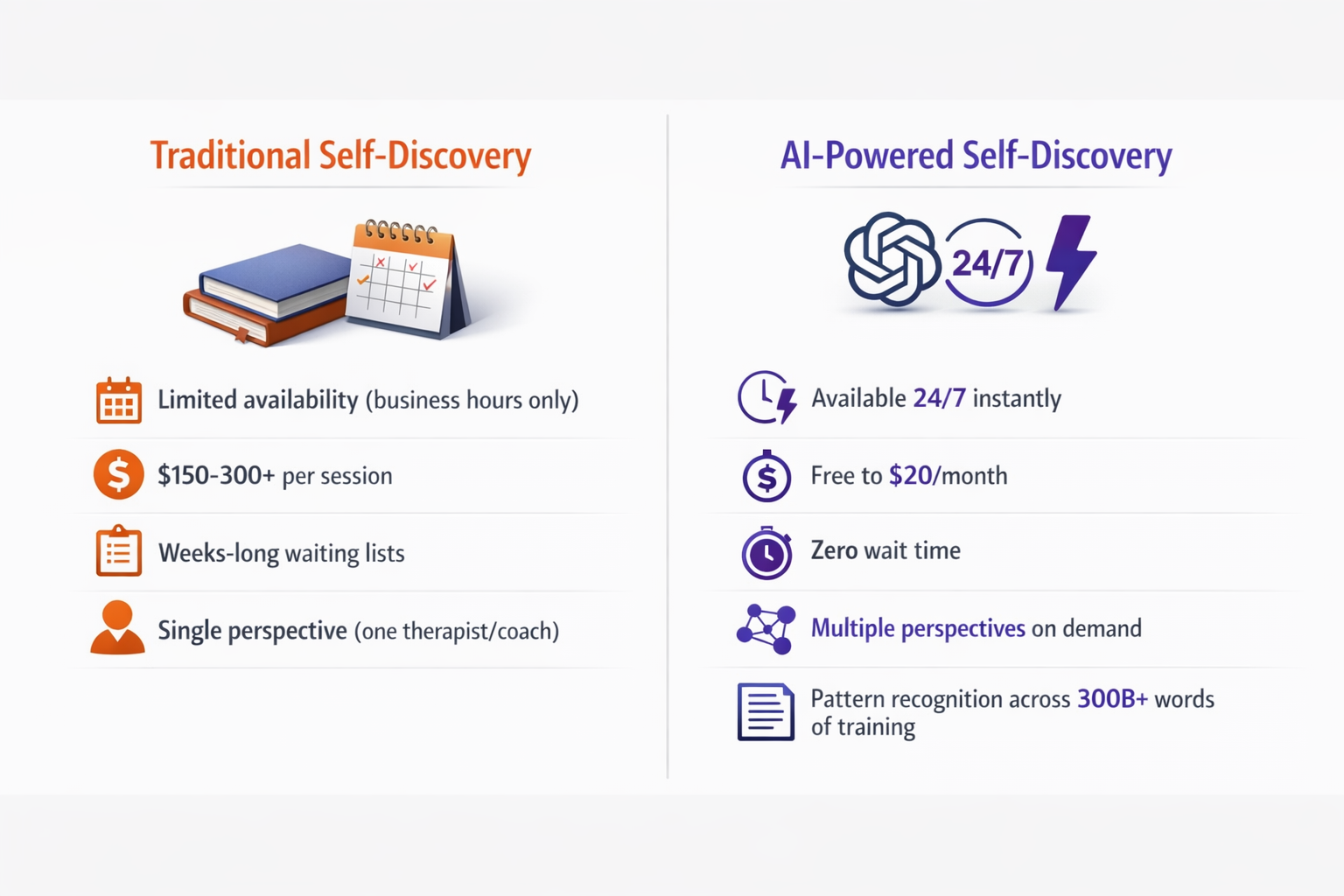
Why LLMs Are Perfect for Self-Discovery (The Science Behind It)
Before we jump into the techniques, you need to understand why language models work so effectively for self-reflection.
Traditional self-help often fails because of three critical barriers: our own blind spots, judgment from others, and the high cost of professional coaching or therapy.
LLMs eliminate all three.
Key Insight: According to OpenAI's comprehensive 2025 study of 1.5 million conversations - The largest consumer AI usage study ever released - women now make up 52% of ChatGPT users, up from just 37% in January 2024. This dramatic shift reveals that people are discovering value far beyond technical applications, with personal growth and self-reflection conversations driving major adoption growth.
Here’s what makes LLMs uniquely powerful for self-discovery:
Zero judgment, infinite patience. An LLM doesn’t get tired of your questions, doesn’t form opinions about you, and maintains complete confidentiality. You can explore the darkest corners of your psyche without fear of judgment.
Pattern recognition at scale. These models were trained on 300 billion words from books, websites, and human conversations. They can identify behavioral patterns and psychological frameworks that would take years of therapy to uncover.
Available 24/7. Unlike human coaches or therapists, you can access an LLM whenever inspiration strikes – at 3 AM when you can’t sleep, during your lunch break, or while traveling.
Miguel Thorpe, a university student featured in educational research, integrated AI into his daily routine and experienced remarkable personal growth. His grades improved, but more importantly, he gained clarity about his life direction that had eluded him for years.
The secret? He treated the LLM not as a tool for answers, but as a tool for asking better questions.
“LLMs aren’t tools for getting answers. They’re tools for asking better questions about yourself.”
Tip #1: The “Biographical Timeline” Method
Real Example:
Prompt: "I'm going to share key moments from my life from ages 5-30. After I'm done, I want you to analyze these events and identify recurring themes, patterns in how I respond to challenges, and potential blind spots I might have. Ready?" Then share 10-15 specific events with emotional context. What happened: Sarah, a marketing professional, discovered that she consistently avoided leadership opportunities not because she lacked ability, but because childhood experiences made her associate leadership with conflict and loneliness.
The LLM excels at connecting dots across decades that you simply can’t see when you’re inside the story.
Pro Tip: Include emotional responses to events, not just the facts. "Started new job" gives the AI nothing to work with. "Started new job feeling excited but also terrified I'd be exposed as a fraud" reveals imposter syndrome patterns the AI can identify across your timeline.
This technique leverages what psychologists call “narrative identity” – the stories we tell ourselves about ourselves. By externalizing your narrative to an AI, you gain perspective that’s impossible to achieve alone.
Tip #2: Pattern Recognition Through Conversation History
Here’s where things get fascinating.
If you’ve been using ChatGPT or Claude for a while, you’ve already created a goldmine of self-discovery data – you just haven’t analyzed it yet.
According to recent usage data, the average ChatGPT session lasts nearly 14 minutes, and message volume has grown 5.8x faster than user growth – meaning people are engaging more intensively over time. That’s potentially thousands of words revealing your interests, concerns, problem-solving approaches, and thinking patterns.
Surprising Stat: ChatGPT now processes over 6.1 billion visits monthly as of late 2025. Each conversation is a window into human psychology, and YOUR conversations are a window into yours.
Try this exercise:
Step 1: Start a new conversation and ask your LLM to analyze your conversation history (if the LLM has access to it, like ChatGPT with memory enabled).
Step 2:
Use this prompt: “Based on all our previous conversations, what patterns do you notice in:
(a) The types of problems I bring to you,
(b) How I frame questions,
(c) The topics I avoid,
(d) The areas where I seek the most help?”
Step 3: Follow up with: “What does this suggest about my underlying values, fears, and priorities?”
Real Discovery:
James, a software engineer, noticed he only asked ChatGPT about technical problems and productivity hacks - never about relationships, emotions, or creative pursuits. This pattern revealed he was compartmentalizing his life and avoiding emotional development entirely. The realization led him to start therapy and reconnect with creative hobbies he'd abandoned years ago.
Your conversation history is like an unconscious journal. The LLM can read between the lines in ways
you can’t.
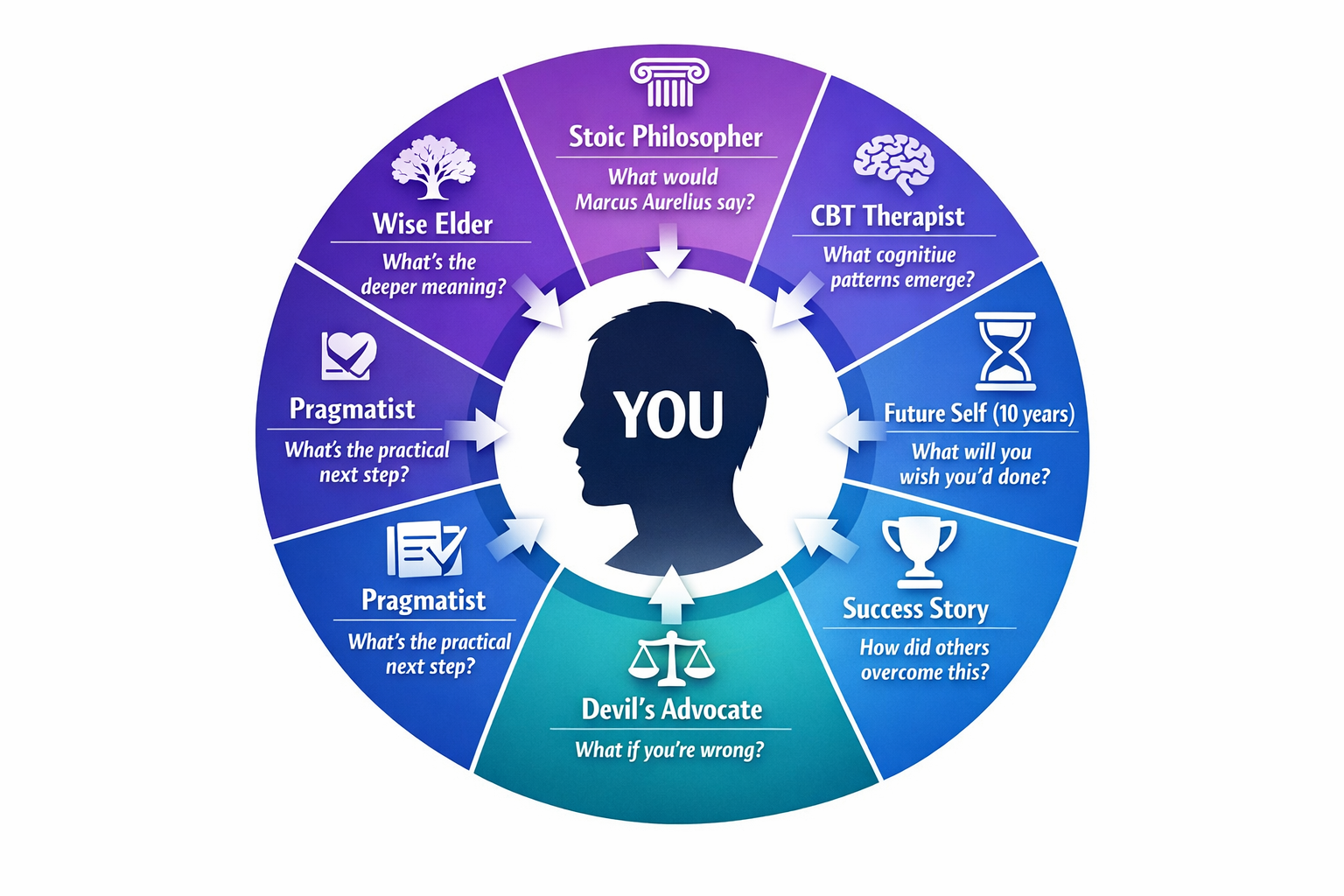
Tip #3: The “Multiple Perspectives” Technique
One of the most powerful capabilities of LLMs is their ability to inhabit different perspectives simultaneously.
Instead of getting advice from one angle, you can get it from ten.
Here’s the framework:
The Prompt Template: "I'm facing [specific situation]. Please analyze this from the perspective of: 1) A Stoic philosopher, 2) A cognitive behavioral therapist, 3) My future self looking back 10 years from now, 4) Someone who has successfully navigated this exact challenge, 5) A devil's advocate who disagrees with my current approach. What unique insights does each perspective reveal?"
This isn’t about getting confirmation for what you already believe. It’s about deliberately seeking contradictory viewpoints to challenge your assumptions.
Esther Jacobs, a speaker and author, used this technique and described ChatGPT as seeing her like “Mary Poppins meets Lara Croft” – a free spirit who appears anywhere but might be using freedom as an escape from deeper connection.
That single observation, generated by asking for multiple perspectives on her life patterns, changed how she approached relationships and professional commitments.
Tip #4: Emotional Mapping Sessions
Most people treat emotions as noise to be suppressed.
LLMs can help you treat them as data to be decoded.
The technique is simple but requires honesty: Throughout your day, whenever you feel a strong emotion (positive or negative), note it. At the end of the week, share all these emotional moments with your LLM and ask it to create a map.
Specific prompt: "I'm going to share 20 moments from this week when I felt strong emotions. For each, I'll describe the situation, the emotion, and my response. Please identify: (a) Emotional triggers I'm not aware of, (b) Unmet needs these emotions might represent, (c) Patterns in how I suppress or express different emotions, (d) Healthier ways I could respond to each trigger."
What This Reveals:
A teacher named Rachel discovered she felt anxiety every time her opinions differed from her friends’ opinions – but only with certain friends. The AI helped her realize she had different versions of herself for different people, and the anxiety was the internal conflict of maintaining these personas.
This insight led to more authentic relationships and significantly reduced her social anxiety.
The power here is in the volume of data. One emotional incident might be random. Twenty incidents reveal a pattern. The LLM spots those patterns faster than any human could.
Research Backing: Clinical studies of expressive writing show significant reductions in stress, anxiety, and depression across more than 4,000 participants, with long-term benefits. AI-enhanced journaling amplifies these benefits through pattern recognition that humans can't match.
Tip #5: The Values Extraction Exercise
Ask someone “What are your core values?” and you’ll get generic responses: family, honesty, success.
Those aren’t your real values. They’re the values you think you should have.
Your real values are revealed through your decisions, not your declarations.
Here’s how to use an LLM to extract your actual values:
Share 10 difficult decisions you’ve made. Include decisions you regret, decisions you’re proud of, and decisions you’re conflicted about. Explain what you chose and why.
Ask the LLM: “Based solely on the choices I made (not the reasons I gave), what values am I actually prioritizing? Where do my stated intentions conflict with my revealed preferences?”
Research Finding: According to cognitive science research, humans are exceptionally poor at self-assessment. We consistently rate ourselves as more ethical, competent, and consistent than our behavior demonstrates. An AI analyzing your decisions doesn't have this bias - it only sees what you actually did.
This exercise is uncomfortable because it often reveals gaps between who we think we are and who we actually are through our choices.
But that discomfort is where growth begins.
Advanced Move: After identifying your revealed values, ask: "If I wanted to align my future decisions with [your ideal values], what specific behavioral changes would be required?" The LLM can create an actionable roadmap.
Tip #6: Decision-Making Analysis
Every decision you make reveals your decision-making algorithm.
Most people never examine this algorithm – they just run it automatically.
LLMs can reverse-engineer your decision-making process by analyzing past choices and predicting how you’ll decide in the future.
Try this:
- Describe 5-7 significant decisions (career changes, relationship decisions, financial choices, geographic moves)
- For each, explain: What factors you considered, what you ultimately chose, how it turned out
- Ask: “Based on these decisions, what is my decision-making pattern? What do I overvalue? What do I undervalue? What blind spots appear in my process?”
- Then present a current decision you’re facing
- Ask: “Given my pattern, predict what I’m likely to choose and explain whether that serves my long-term interests”
Case Study: David, an entrepreneur, realized through this exercise that he consistently chose novelty over stability - launching new projects before finishing existing ones. The pattern explained his unfulfilled potential despite high intelligence and work ethic. The AI's prediction: "You're likely to abandon your current profitable business to chase this new idea. Based on your history, you'll be excited for 6-8 months, then repeat the pattern." That prediction was so accurate and uncomfortable that David finally committed to seeing one project through to completion.
This isn’t about the LLM making decisions for you. It’s about becoming conscious of the unconscious patterns driving your choices.
Tip #7: The “Shadow Work” Prompts
In Jungian psychology, the “shadow” represents the parts of ourselves we deny or repress.
LLMs are exceptionally good at helping you explore your shadow because they won’t judge what they find.
Here are prompts specifically designed for shadow work:
“What traits do I criticize most harshly in others? What might that reveal about rejected parts of myself?”
“What am I most afraid people will discover about me? Why is that fear so powerful?”
“If someone accused me of [your worst fear about yourself], and it was partially true, what would I need to accept about myself?”
“What desires or ambitions do I dismiss as unrealistic or inappropriate? What would pursuing them reveal about my authentic self?”
Warning: This work can bring up intense emotions. Start small. Don't dive into your deepest wounds in your first session. Shadow work is like strength training - you build up to heavier weights gradually.
Tip #8: Skill and Talent Inventory
You have talents you don’t recognize because they come so naturally you assume everyone can do them.
Here’s how to uncover them:
Prompt structure:
“I’m going to describe tasks that feel easy to me but seem difficult for others. Please identify potential talents or strengths these activities reveal, including ones I might be undervaluing.”
Then list 15-20 things you can do easily that you’ve noticed others struggle with. Include seemingly trivial things:
- “I can read a room and know who’s upset even if they’re hiding it”
- “I can look at complex systems and immediately see inefficiencies”
- “People tell me I’m a good listener but I don’t do anything special”
- “I can explain technical concepts to non-technical people easily”
- “I notice patterns in data before I even consciously look for them”

The LLM will categorize these abilities and often identify a meta-skill you didn’t realize you had.
Discovery Example: Marcus thought he was just "okay" at his marketing job. When he listed what came easily to him, the pattern became clear: exceptional pattern recognition, intuitive understanding of human behavior, and ability to simplify complexity. The AI identified this cluster as strategic thinking - a highly valuable skill he was completely unaware he possessed at an elite level.
Tip #9: Relationship Pattern Decoder
Your relationship patterns repeat until you see them.
An LLM can decode these patterns with uncomfortable accuracy.
The exercise: Describe 5-6 significant relationships (romantic, friendships, professional) that ended or changed dramatically. For each, explain:
- How it started (what attracted you)
- The dynamic during the relationship
- How and why it ended or changed
- Your emotional response and interpretation
Then ask: “What patterns do you see in who I’m attracted to, how I behave in relationships, and how they typically end? What role do I consistently play? What needs am I trying to meet through relationships that might be better met elsewhere?”
Psychological Principle: Attachment theory suggests we unconsciously recreate childhood relationship dynamics throughout our lives. An LLM can identify these patterns across your relationship history, especially when you're too close to the situation to see them clearly.
This is one of the most emotionally challenging exercises, but also one of the most transformative.
One woman discovered she consistently chose partners who needed “fixing” because being the helper allowed her to avoid her own vulnerabilities. She’d never made this connection despite years of failed relationships.
Tip #10: The “Future Self” Dialogue
This technique leverages the LLM’s ability to role-play with remarkable accuracy.
The setup: Provide detailed information about yourself – your current situation, goals, challenges, personality traits, and life context. Then ask the LLM to assume the role of your future self 10 years from now who has achieved the life you want.
The dialogue: Have a conversation with this future self. Ask questions like:
- “What was the most important change I needed to make?”
- “What was I worried about that didn’t actually matter?”
- “What opportunity did I almost miss?”
- “What advice do you have for me right now?”
- “What pattern did I need to break first?”
Powerful Moment: Jennifer, a corporate lawyer considering leaving to start a business, had this exchange with her "future self": J: "Was it worth the financial risk?" Future Self: "You're asking the wrong question. The real risk was staying in a career that was slowly deadening your spirit. The financial challenges were temporary. The regret would have been permanent." That response gave her the clarity to make a decision she'd been avoiding for three years. The magic here isn't that the AI knows your future - it's that it can extrapolate from your stated values and patterns to show you a path your current fears might be obscuring.
Tip #11: Limiting Belief Excavation
Limiting beliefs operate below conscious awareness.
You can’t change what you don’t see.
LLMs excel at identifying limiting beliefs embedded in your language patterns.
The process:
- Have a conversation with the LLM about an area where you feel stuck (career, relationships, creativity, health)
- Speak freely for 5-10 minutes about why you haven’t achieved what you want in this area
- Then ask: “Analyze my explanation. What limiting beliefs are embedded in my language? What am I assuming that might not be true? What possibilities am I not considering because of these beliefs?”
Key Phrases to Watch For: The AI will often catch limiting beliefs in statements like "I'm just not the type of person who...", "In my experience, people always...", "I could never...", "It's just how I am...", "That works for others but not for me because..."
These phrases reveal unconscious rules you’ve created about what’s possible for you.
Once identified, you can test them. Most limiting beliefs crumble under examination – they’re based on old data or isolated incidents you’ve generalized into universal laws.
Tip #12: Personality Framework Integration
Personality frameworks like Myers-Briggs, Enneagram, Big Five, or StrengthsFinder provide useful vocabularies for understanding yourself.
But most people stop at knowing their type.
LLMs can help you go deeper:
Advanced prompt:
“I’m an [Enneagram Type 4 / INFP / High Openness-Low Conscientiousness]. Given this type, what are the predictable pitfalls I face? What strengths am I likely underutilizing? How might my type be limiting me in ways I don’t see? What would growth look like specifically for my type?”
Then go further: “Based on everything you know about me from our conversations, do you think this type fully captures me? What aspects of my personality don’t fit the type? What might that discrepancy reveal?”
Integration Example: Tom identified as an INTJ but the AI noticed his decision-making was far more emotionally driven than the type suggests. This led to the discovery that he'd been suppressing his emotional intelligence to fit an identity he thought was more valuable.
Embracing his full personality (thinking AND feeling) made him more effective, not less.
Personality types are maps, not territories. The LLM can help you see where the map doesn’t match your actual terrain.
Tip #13: The Journaling Enhancement Protocol
Journaling is powerful for self-discovery, but most people either quit after a few days or write without structure.
LLMs can supercharge your journaling practice.
Method 1: Prompt Generation
Ask your LLM to create 30 days of journaling prompts customized to your current challenges and goals. For example: “I’m working on improving my confidence and reducing anxiety. Create 30 unique journaling prompts that will help me explore these areas deeply.”
Method 2: Journal Analysis
After a week or month of journaling, share your entries and ask: “What themes emerge? What am I avoiding? What patterns do you notice in my thoughts and feelings? What insights am I missing?”
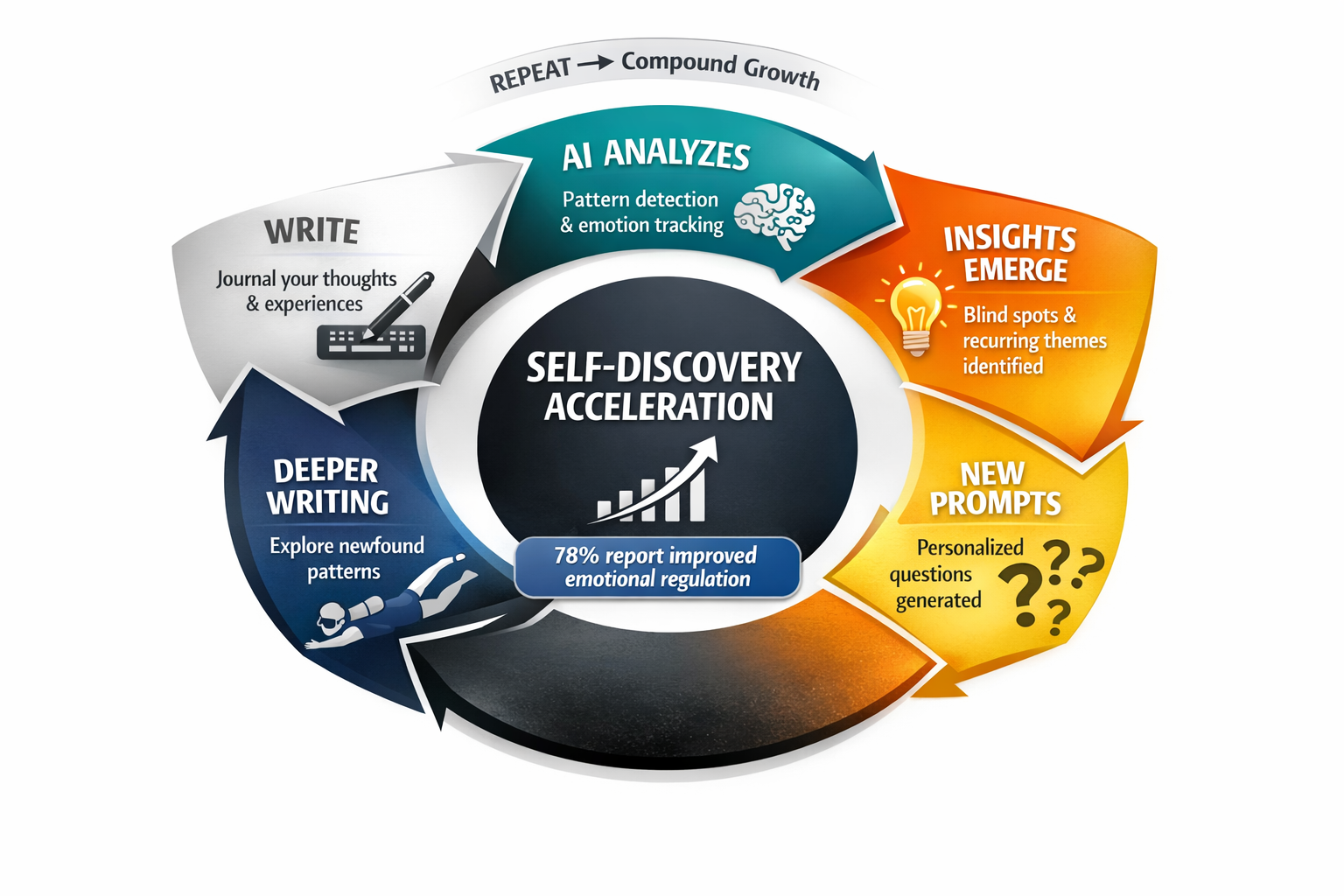
Method 3: Framework Suggestions
Apps like Reflection, Mindsera, and Rosebud use AI to guide journaling with proven frameworks. Ask your LLM to teach you various journaling frameworks and recommend which ones match your personality and goals.
Evidence-Based Benefit: A 2024 study revealed that 78% of users who integrated AI-driven journaling into their routines reported improved emotional regulation and reduced anxiety levels. Research shows that 88% of journalers report enhanced focus and clarity, while regular journaling increases goal achievement by 42%.
Tip #14: Communication Style Analysis
How you communicate reveals how you think.
Most people have never analyzed their communication patterns because they’re too busy communicating to step back and observe.
The exercise: Share examples of how you communicate in different contexts – emails to colleagues, texts to friends, presentations, difficult conversations, casual chats. Include both written and descriptions of verbal communication.
Ask the LLM: “Analyze my communication style. What patterns do you notice? When am I most and least effective? What communication habits might be creating problems I don’t see? How does my style change depending on context or audience?”
The LLM can identify things like:
- Over-apologizing that undermines your authority
- Using complex language to create distance
- Avoiding directness in conflict situations
- Dominating conversations vs. collaborative dialogue
- Passive-aggressive patterns you’re unaware of
Real Result: Amanda discovered she used qualifiers like "just," "maybe," and "I think" in 80% of her professional emails, especially when communicating with men. This pattern was invisible to her but immediately obvious to the AI. Awareness alone helped her communicate more directly, and her professional relationships improved dramatically.
Tip #15: The “Stress Response” Mapping
You don’t really know yourself until you know how you respond to stress.
Your stress response reveals your deepest patterns and most ingrained coping mechanisms.
The mapping process:
- Describe 8-10 high-stress situations you’ve experienced across different life domains (work deadlines, relationship conflicts, financial pressure, health scares, etc.)
- For each, describe not just what happened but how your body felt, what thoughts you had, and what actions you took
- Ask: “What is my stress response pattern? How does it help me? How does it hurt me? What am I trying to protect when I respond this way? What would a healthier response look like?”
Physiological Detail Matters: Don't just say "I felt stressed." Describe it: "My chest tightened, I couldn't focus, I got irritable and snapped at people, I couldn't sleep." These physical details help the AI identify whether you're experiencing fight, flight, freeze, or fawn responses.
Understanding your stress pattern is like understanding your operating system under load. It reveals your psychological architecture.
Tip #16: Goal Alignment Checker
Most people’s goals aren’t actually their goals.
They’re inherited from parents, culture, social pressure, or past versions of themselves that no longer exist.
LLMs can help you audit your goals for authenticity.
The audit: List all your major goals (career, relationship, financial, health, personal development). For each goal, write:
- When you first set this goal
- Why you think you want it
- Who would be pleased if you achieved it
- How you actually feel when you work toward it
Then ask: “Which of these goals seem authentically mine versus imposed by external expectations? Where do I see misalignment between what I say I want and what my behavior suggests I actually value? Which goals might actually belong to a past version of me?”
Eye-Opening Discovery: Carlos had "make VP by 40" as a major goal. The AI pointed out that in every conversation, he expressed excitement about teaching and mentoring, but dread about management responsibilities. The VP goal was his father's dream, not his. Recognizing this freed him to pursue a career path he actually wanted - becoming a technical trainer.
“Achievement without fulfillment happens when you’re chasing someone else’s goals instead of your own.”
Tip #17: The “Blind Spot” Reveal
By definition, you can’t see your blind spots.
But an LLM analyzing your language patterns, choices, and contradictions can spot them.
Direct approach: “Based on everything I’ve shared with you, what blind spots do you think I have? What patterns do I seem unaware of? What contradictions appear between what I say I value and what my behavior suggests? Where am I likely deceiving myself?”
This prompt requires courage because the answer might sting.
But it’s also one of the most valuable questions you can ask.
Cognitive Science Finding: The Dunning-Kruger effect shows we're particularly bad at assessing our own competence. Similarly, we have massive blind spots about our behavior, motivations, and impact on others. External observation (even from AI) is often more accurate than self-assessment.
One user described asking this question as “the AI holding up a mirror I’d been avoiding for years.” The insights were uncomfortable but led to breakthrough changes in multiple life areas.
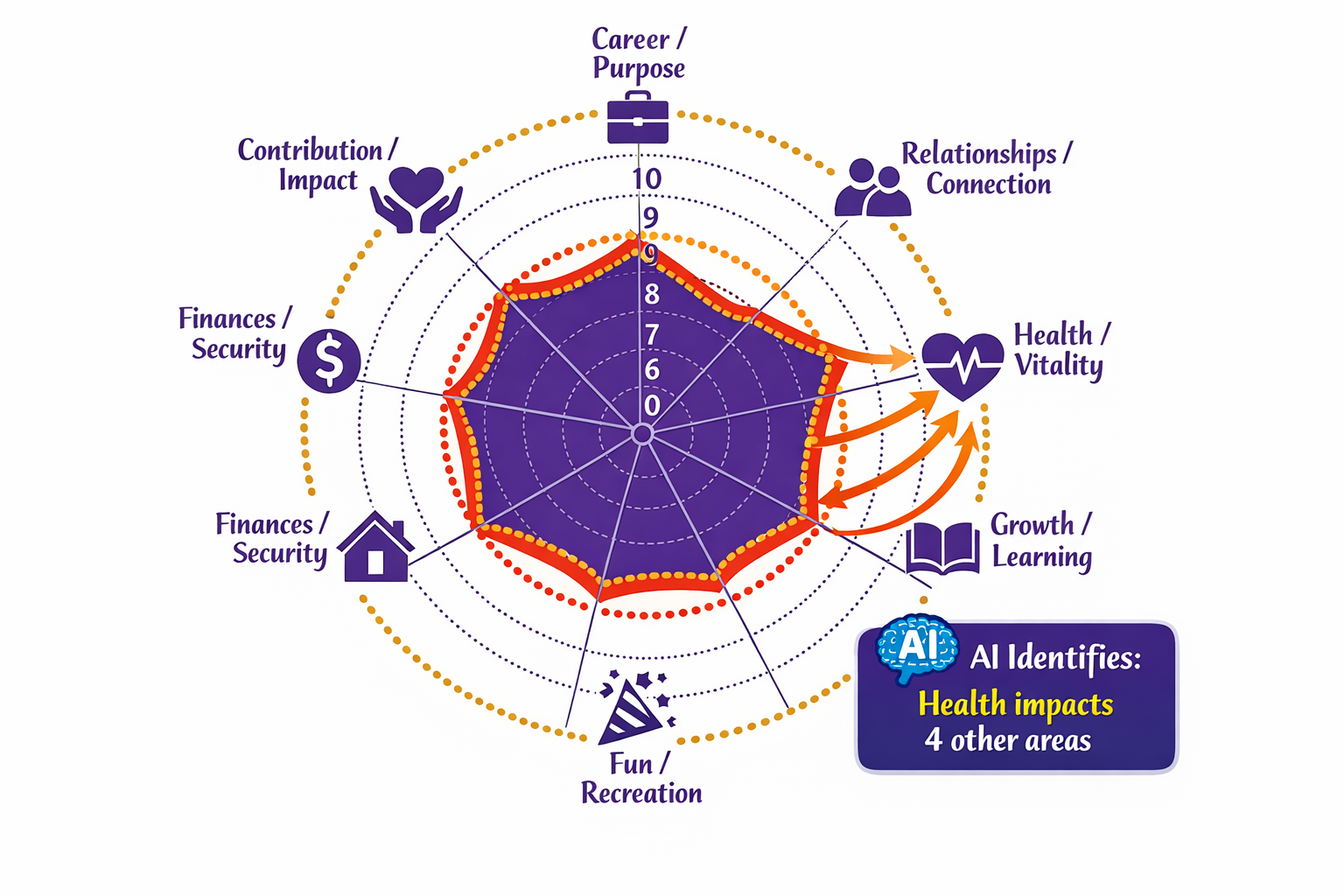
Tip #18: Life Satisfaction Audit
People often feel vaguely dissatisfied but can’t pinpoint why.
A structured life audit with AI assistance can illuminate exactly where the dissatisfaction originates.
The framework: Rate your satisfaction (1-10) in these life domains:
- Career / Purpose
- Relationships / Connection
- Health / Vitality
- Growth / Learning
- Fun / Recreation
- Environment / Living Situation
- Finances / Security
- Contribution / Impact
For each rating, explain why you gave that score.
What’s working?
What’s not?
Ask the LLM:
“Based on these ratings and explanations, what areas need immediate attention? What interconnections do you see – how might low satisfaction in one area be affecting others? What’s one change in each low-rated area that could create the biggest improvement?”
Tip #19: The “Ideal Day” Design
What you do with unrestricted time reveals your true priorities.
This exercise helps you design a life that aligns with those priorities.
The prompt:
“I’m going to describe my ideal day – from waking up to going to sleep – if I had no obligations and unlimited resources. Please analyze this ideal day and tell me: What does it reveal about my core values and needs? What elements could I incorporate into my actual life right now? What’s stopping me from living more like this?”
Then describe your ideal day in vivid detail. What time do you wake up? What do you do first? Who are you with? What activities fill your day? How do you feel?
Insight Example: Priya's ideal day was 70% outdoors and focused on physical activity, creativity, and small-group connections. Her actual life was 90% indoors, sedentary, and isolated. The AI helped her identify small changes (morning walks, joining a hiking group, moving her desk near a window) that brought her actual life closer to her ideal without requiring a complete life overhaul. Most people think they need a total life redesign when often they just need to incorporate elements of their ideal day into their current reality.
Tip #20: Cognitive Bias Identifier
We’re all running biased mental software, but we think we’re being objective.
LLMs can identify the specific cognitive biases distorting your thinking.
How it works: Describe a situation where you’re making a judgment or decision. Explain your reasoning in detail – why you think what you think, what evidence you’re considering, what conclusions you’re drawing.
Then ask: “What cognitive biases might be influencing my thinking here? Am I exhibiting confirmation bias, availability heuristic, sunk cost fallacy, anchoring, or other biases? What evidence am I ignoring that contradicts my position?”
Common Biases the AI Often Identifies:
-
-
Confirmation bias: Only seeing evidence that supports your existing beliefs
-
Recency bias: Overweighting recent events
-
Fundamental attribution error: Attributing others' behavior to character but your own to circumstances
-
Dunning-Kruger effect: Overconfidence in areas where you have limited knowledge
-
Being aware of your cognitive biases doesn't eliminate them, but it helps you compensate for them when making important decisions.
Tip #21: Energy Source and Drain Analysis
Energy management is more important than time management.
But most people don’t know what actually energizes versus depletes them.
The tracking method: For one week, note every activity and rate your energy before and after (scale of 1-10). Include work tasks, social interactions, leisure activities, everything.
At the end of the week, share this data with your LLM and ask:
- “What patterns emerge about what energizes vs. drains me?”
- “Are there surprises – things I thought would energize me but don’t, or vice versa?”
- “How could I restructure my days to maximize energy-giving activities and minimize or better manage energy-draining ones?”
- “What might be draining my energy that isn’t obvious (certain people, environments, times of day)?”
Surprising Finding: Michael, an extrovert, discovered that not all social activities energized him. Large group events drained him while deep one-on-one conversations energized him. He'd been forcing himself to network events thinking he "should" enjoy them as an extrovert. Shifting to coffee meetings and dinner parties with friends tripled his social satisfaction while halving his social exhaustion.
Tip #22: The “Character Creation” Method
One of the most creative self-discovery techniques is asking the LLM to analyze you as if you were a character in a story.
The prompt:
“Based on everything you know about me, if I were a character in a novel, movie, or TV series, describe my character arc.
What genre would my story be? Who am I at the beginning?
What’s my central conflict?
What do I need to learn?
How might my story evolve?
What would be a satisfying resolution to my character arc?”
Why This Works: Narrative distance gives you perspective on your life that's impossible to achieve when you're inside it. Seeing yourself as a character helps you identify patterns, themes, and potential trajectories you can't see from the first-person view.
This exercise often reveals that you’re stuck in Act 2 of your life story – in the middle of conflict and growth – when you thought you should already be in the resolution phase.
Or it might show you that you’re playing a supporting character in someone else’s story instead of being the protagonist of your own.
Tip #23: Progress Tracking Through AI Reflection
Personal growth is hard to measure because you’re changing while trying to measure the change.
LLMs can serve as external witnesses to your evolution.
The system: Every month, have a “reflection session” with your LLM where you:
- Describe significant events, challenges, and wins from the past month
- Share what you learned about yourself
- Identify patterns you notice in your behavior or thinking
- Set intentions for the next month
After 3-4 months, ask: “Review my past monthly reflections. What progress do you see? What patterns persist? What has genuinely changed versus what remains stuck? What does my trajectory suggest about where I’m headed?”
Bonus Technique: Save these monthly reflections in a document. Once a year, ask the AI to create a "year in review" analyzing your growth trajectory. Seeing 12 months of evolution in one analysis is extraordinarily powerful.
The LLM has perfect memory of your past states. It can show you progress you’ve forgotten or minimized, and it can highlight recurring issues you keep thinking you’ve solved but haven’t.
Tip #24: The “Unconventional Strengths” Finder
Standard strength assessments ask about conventional skills.
But some of your most valuable strengths are things no assessment would think to ask about.
The discovery method: Ask people who know you well: “What do I do that seems unremarkable to me but impressive to you?” Collect 10-15 responses.
Share these with your LLM along with examples of situations where these abilities showed up.
Ask:
“What unconventional strengths do these observations reveal? How could these abilities be leveraged in ways I haven’t considered? What careers, projects, or life paths would particularly benefit from these specific strengths?”
Unconventional Strength Discovery: Friends kept telling Lisa she was amazing at "making people feel seen." She thought this was just basic politeness. The AI identified it as exceptional emotional intelligence combined with genuine curiosity - a rare combination that would make her extraordinary at leadership, coaching, or user research. She'd been working in data analysis feeling unfulfilled. Within a year of this discovery, she transitioned to UX research where her "unremarkable" skill became her superpower.
Your superpowers often hide in plain sight, disguised as things that “just come naturally.”
Tip #25: Integrating Multiple LLMs for Deeper Insights
Different LLMs have different strengths and “personalities.”
For maximum self-discovery, use multiple models and compare their analyses of you.
The multi-model approach:
- Have a deep self-discovery conversation with ChatGPT
- Take the same information to Claude and ask for its analysis
- If you have access to others (Gemini, Perplexity, etc.), get their perspectives too
- Compare the responses – Where do they agree? Where do they differ?
Agreement across multiple models suggests robust insights. Divergence suggests areas where the data about you is ambiguous or contradictory – which is useful information in itself.
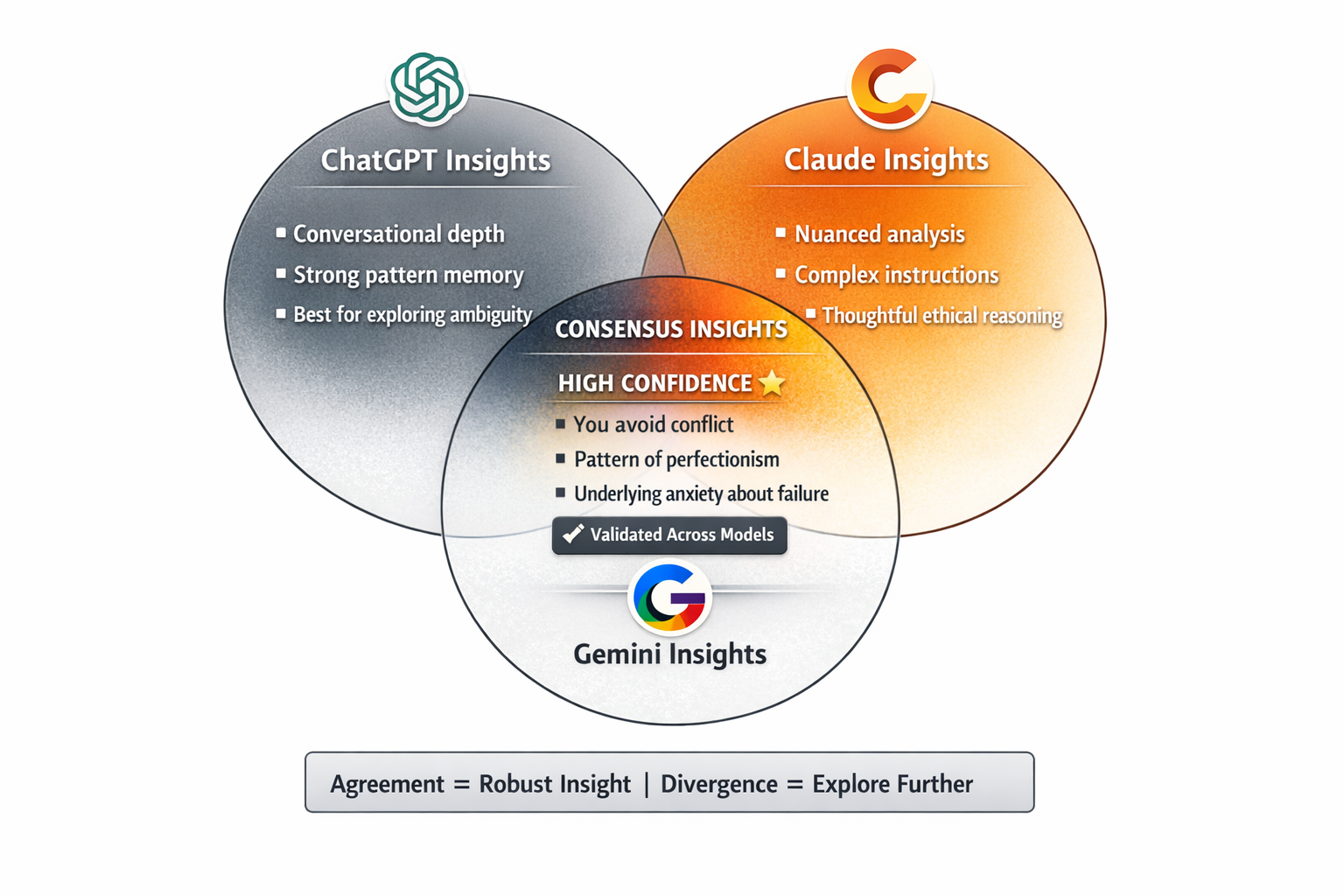
Each LLM will notice different things because they’re trained slightly differently and have different ways of processing information.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
After analyzing hundreds of hours of self-discovery sessions, these are the mistakes that undermine results:
Mistake #1: Seeking Validation Instead of Truth
The LLM will often confirm your existing beliefs if that’s what you’re fishing for. Ask questions that might challenge you, not just questions that make you feel good.
Mistake #2: Being Vague
Generic input produces generic insights. “I want to be happier” gives the AI nothing to work with. “I feel emptiest on Sunday evenings after scrolling social media for two hours even though I planned to work on my side project” gives it everything.
Mistake #3: Stopping at the First Layer
The first response is rarely the deepest insight. Always ask follow-up questions: “What else?” “What am I not seeing?” “Challenge that assumption.” “What’s beneath that pattern?”
Mistake #4: Not Taking Action
Insight without action is just interesting information. After each discovery, ask: “What is one concrete action I can take in the next 24 hours based on this insight?”
Mistake #5: Confusing the AI’s Confidence with Accuracy
LLMs respond with confidence even when they’re uncertain. Always verify insights against your own experience and judgment. The AI is a tool for reflection, not an oracle.
Frequently Asked Questions

Want to grow your business online?
I’m Ahmed Sohail, and I’m helping businesses grow with determined results. My question is, does your business needs growth?
Contact Now

